Copyright ⓒ 2014 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
Rh factor and Rh incompatibility Rh 인자와 Rh 부적합

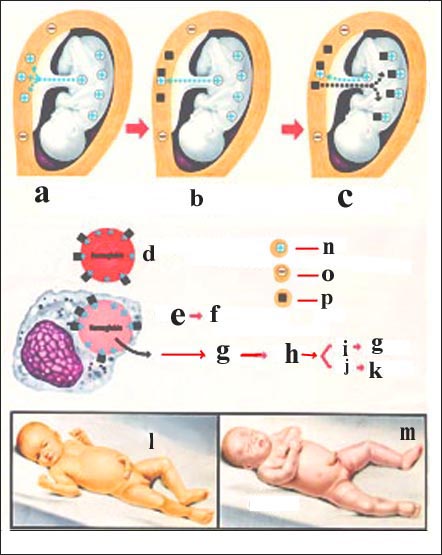
The mechanism of fetal erythroblastosis and hemolytic anemia and jaundice in the fetus and newborn due to Rh incompatibility A-Rh-positive blood enters the blood of pregnant women with Rh-negative blood. The red blood cells in the blood of the b-pregnant are sensitized and Rh antibodies are formed. c-If the next fetus’s Rh is positive-Rh antibodies generated in the mother enter the fetus’ blood and react with the fetal’s Rh positive red blood cells. The Rh antibody attaches to the red blood cells of the d-fetus. e-red blood cells are destroyed. f- hemolysis occurs. g-hemoglobin is destroyed. Abnormally excessive production of h-bilirubin and anemia occurs. i-skin becomes yellow, and j-jaundice occurs. Indirect bilirubin can be stained in the k-brain. l-nucleus jaundice may develop. m-fetal species, n-Rh positive, o-Rh negative (antigen), p-Rh antibody Source: Ross Laboratories, Columbus, Ohio 43216, Division of Laboratories, USA
Blood types are classified into ABO blood types and Rh factors. And the Rh factor is divided into Rh positive (Rh +) and Rh negative (Rh-). During pregnancy, it is essential to find out if the blood type of pregnant women is A, B, O, or AB, and if the Rh factor is Rh positive or Rh-negative. 85% of white women are Rh-positive, but almost all black and Asian women have Rh-positive.
In 1 in 500 Korean women, the Rh factor is Rh-negative.
If the couple’s Rh factor is Rh positive or Rh negative, the Rh factor of the baby to be born to the couple must be the same as the Rh factor of the mother and father.
When the Rh factor of a pregnant woman is Rh-negative and the husband’s Rh factor is positive, the Rh factor of a baby born to the couple must be Rh-positive or Rh-negative. When the Rh factor of a pregnant woman is Rh-negative and the Rh factor of the fetus is Rh-positive,
Rh antibodies that can destroy fetal red blood cells can be made in the blood of the pregnant woman. And the Rh antibody made in the blood of the pregnant woman passes through the placenta and enters the blood of the fetus, and Rh incompatibility can occur in the fetus.
When the Rh antibody in the pregnant woman’s blood enters the fetal’s blood and the Rh antibody adheres to the fetal’s red blood cells, the fetal’s red blood cells can hemolysis, which can lead to anemia and jaundice in the fetus and newborn.
This jaundice is called neonatal jaundice caused by Rh incompatibility. In general, when anemia or jaundice occurs due to Rh incompatibility, the degree is very severe, and if the anemia or jaundice is not properly treated immediately, it is dangerous to life, and when it is very severe, nuclear jaundice can also occur.
Rh antibodies may continue to be present in the blood of mothers who deliver a fetus with Rh incompatibility. When a woman with Rh antibody and Rh-negative is pregnant with another Rh-positive fetus, the Rh antibody in the woman’s blood can enter the fetus’s blood, causing another Rh incompatibility in the fetus.
When an Rh-negative pregnant woman first conceives an Rh-positive fetus, Rh nonconformity rarely occurs in the fetus.
When an Rh-negative woman first delivers an Rh-positive boy, the woman may or may not develop Rh antibodies at all.
If an Rh-negative woman without Rh antibody gives birth to an Rh-positive child, if the Combs test is negative, the Rh incompatibility does not occur in the fetus when conceived with an Rh-positive fetus.
Prevent. After delivery of the first Rh-positive child, mothers should receive an Rh-immune gammaglobulin injection within 72 hours.
If the husband’s Rh factor is Rh-positive and the wife’s Rh factor is Rh-negative, even when the wife’s miscarriage or abortion surgery, the wife will receive an Rh immune gamma globulin (RhoGAM) injection within 72 hours after abortion or miscarriage. It should be right.
For this reason, when receiving regular pregnancy check-ups, the ABO blood type test and Rh factor of all pregnant women are routinely tested to find out what type of blood they have and whether the Rh factor is positive or negative.
In addition, if the Rh factor of the baby born to the Rh-positive husband and the Rh-negative pregnant woman is Rh-positive or Rh-negative, and if the baby’s Rh factor is positive, the baby’s blood should be tested for combs. Copyright ⓒ 2014 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-본 사이트의 내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
“Parental education is the best medicine.“