- 빈혈이 있는지 알이보기 위해 임신부의 시비시(CBC) 검사한다. Blood test for anemia in pregnant women임신부의 피를 채취해서 임신부가 빈혈이 걸려 있는지 알아보는 헤모글로빈검사나 헤마토크리트, 또는 시비시검사를 할 수 있다.
- 임신부의 ABO 혈액형과 Rh 인자를 알아보는 피검사를 한다 ABO blood type and Rh factor in pregnant womenABO 혈액형 검사도 하고 RH 인자가 양성인지 음성인지 검사하기 위해 임신부의 피를 통상적으로 검사한다.
- 풍진 혈액검사를 한다 Rubella antibody test임신부가 풍진을 앓았던 과거 병력이 있는지, 앓았다면 충진 바이러스 항체가 있는지 알아보기 위해 풍진 항체를 검사 한다.
- B형 간염 검사를 한다. Hepatitis B test
임신부가 B형 간염 바이러스 감염으로 간염을 현재 앓고 있거나 B형 간염 바이러스를 보균하고 있을 수 있다. 분만 중 또는 분만 후 아기가 B형 간염 바이러스에 감염될 수 있다.
그런 이유로 임신 초기에 임신부의 피를 검사해 B형 간염에 걸려 있는지, B형 간염 바이러스 감염을 앓고 낫았는지, B형 간염 바이러스 예방 접종을 받았는지 알아보는 B형 간염 항원, 항체 검사를 통상적으로 한다.
임신부가 B형 간염에 걸려 있거나 B형 간염 바이러스를 보균하고 있는 엄마로부터 아기가 태어나마자 바로 그 아기에게 B형 간염 예방접종을 바로 해 주고 적절한 다른 처치를 취해야 한다. - 매독 혈청검사를 한다. Syphilis Serum test
요즘 임신부가 매독에 걸리는 경우는 드물다. 그러나 임신 초기에 임신부가 매독에 걸리면 임신부의 태아가 임신부로부터 매독균에 감염되여 태아에게 선천성 기형이 생길 수 있다. 또는 저능아로 태어 날 수 있다. 모든 임신부는 임신 초기에 매독에 걸려 있나 알아보기 위해 매독 혈청 피검사를 통상적으로 받아야 한다. - 에이즈 혈액검사를 한다. Human immunodeficiency virus( HIV) infection /AIDS test
난잡한 이성생활을 할 때 인간면역결핍 바이러스에 감염되면 에이즈에 걸릴 수 있다. 또 불결한 주사바늘이나 의료기구를 통해서도 이 바이러스에 감염될 수도 있다.
그리고 인간면역결핍 바이러스에 감염된 피를 수혈받으면 이 병에 걸릴 수 있다. 인간면역결핍 바이러스에 감염된 모체에서 태어난 아기에게 에이즈가 발생할 수 있다. - 혈당검사를 하고 필요에 따라 혈당 내성검사를 한다.Blood glucose test and glucose tolerance test
모든 임신부의 혈당을 통상적으로 또는 선별적으로 검사할 수 있다. 그러나 혈당 내성검사는 선발적으로 하는 것이 보통이다.
임신부가 1형 당뇨병에 걸릴 수 있고, 2형 당뇨병, 또는 임신 유발성 당뇨병에 걸릴 수 있다. 임신을 하기 전에는 당뇨병이 없던 임신부가 임신 된 이후 임신부에게 임신으로 인해 당뇨병이 생길 수 있다. 이런 댱뇨병을 임신 유발성 당뇨병이라고 한다.
임신 유발성 당뇨병은 해산을 한 후 자연적으로 없어지는 것이 보통이다.
임신 유발성 당뇨병은 일종의 임신 합병증이다. 이 병을 진단하기 위해서 당분을 섭취하고 혈당을 측정해서 진단하기도 하고 어떤 의사는 임신 중 매 3개월마다 혈당을 통상적으로 측정한다. - 그 외
- 태아의 생명이나 건강에 위험한 어떤 기형이 태아에게 있을 때
- 앞으로 태어날 아기의 생명이나 건강에 위험한 췌 낭포성 섬유종이나 테이-싹스병 등 어떤 유전병 등이 태아에게 생길 가능성이 있을 때
- 태아 울트라사운드 검사에 다운 증후군, 삼염색체성 18 이나 삼염색체성 13 등 염색체 이상으로 생긴 병이 태아에게 있을 가능성이 있을 때
- 태아가 다운 증후군에 걸려있는지 알기 위해 모체 혈청 알파 페토프로테인 검사를 선별적으로 했을 때 그 결과가 비 정상적으로 높을 때
- 태아의 성장이 지연 내지 비정상적일 때
- 양수 감염으로 조기 분만이 될 때
- 임신부가 톡소플라스모시스에 감염(톡소플라스마증)되어 있거나 사이토메갈로 바이러스나 팔보 바이러스 등에 감염됐을 때 고 위험성 임신이라고 할 수 있다. 이 때 모체에게 감염 병을 일으킨 병원체가 태아에게도 감염될 수 있다.
- Rh 부적합으로 태아의 적혈구가 파괴될 때
- 태아의 폐 발달의 정도를 알아보기 위해서
- 그 외
Prenatal ultrasound tests
| 울트라사운드 검사의 종류 |
산전 울트라사운드 검사에는 일반적 산전 울트라사운드 검사, 특별한 이유가 있을 때 하는 선별적 울트라사운드 검사와 정밀 산전 울트라사운드 검사로 나눌 수 있다. 일반적 산전 울트라사운드 검사로 태아의 임신 주수, 크기와 자세, 심박동, 태반의 위치, 양수의 양 등을 알아본다. 태아의 선천성 심장 기형 등 특정 기관에 어떤 이상이 있는지 알아볼 때는 정밀 산전 울트라사운드 검사를 하는 것이 보통이다. 그외 필요에 따라 여러 가지의 산전 울트라사운드 검사를 할 수 있다.
| 울트라사운드 검사의 원리 |
초음파 검사 기계 (울트라사운드 검사 기계)에 달린 프로브에서 약 1 to 5 메가헬즈(Megahertz) 정도의 초음파(울트라사운드)가 나올 수 있다. 그 초음파의 진동이 신체 내에 있는 액체, 연조직, 골 등 조직 속으로 이동하게 된다.
초음파의 진동이 신체 내 각 조직 속으로 이동하는 동안 신체의 각 조직에 부딪히게 된다. 조직의 경도가 신체의 각 조직의 종류에 따라 다소 다르다.
초음파의 진동이 경도가 아주 높은 조직에 부딪히면 더 이상 진동이 진행되지 않고 진동이 반향되고 경도가 아주 낮은 조직에 부딪히면 진동이 계속 더 진행 되다가 결국에는그 것도 반향된다.
다시 설명하면 신체의 각 조직의 경도에 따라 초음파의 일부는 더 일찍 반향되고 일부는 더 계속 진동되다가 결국에는 부딪힌 조직의 경도에 따라 늦게서 반향될 수 있다. 또 그 중 일부의 다른 초음파는 더 이상 진동될 수 없고 반향될 때까지 더 계속 진동된다.
초음파 기계에 달려있는 프로브에서 검사 대상까지의 거리, 초음파가 반향되는 시간, 반향의 강도 등이 검사 기계의 기록지에 기록되어 육안으로 볼 수 있게 초음파 검사 사진을 만들 수 있다.
이런 원리를 이용해서 만든 것이 바로 울트라사운드 검사이다.
| 울트라사운드 검사를 복부에서도 하고 질강에서도 한다. |
의학에서 X 선 검사가 우리 인류에게 준 값어치는 헤아릴 수 없을 정도로 크다. 또한 울트라사운드 검사가 우리 인류에게 주는 유용한 가치는 역시 전체 의학분야 뿐만 아니라 다른 분야에서도 헤아릴 수 없이 지대하다. 특히 산과와 주산기과에서는 울트라사운드 검사의 가치는 너무도 크다.
울트라사운드 검사를 받을 때 태아들에게도 임산부들에게도 통증을 주지 않고, 또 이 검사는 침입성 검사 가 아니고 피검사자의 육체에 해롭지 않다.
임신 주수에 따라 울트라사운드 프로브를 복부에 놓고 검사를 하고 임신 제1 삼개월기 동안 울트라사운드 검사를 할 때는 특별히 만든 울트라사운드 프로브를 질강 속에 넣고 검사하기도 한다.
임신 제1 삼개월기 이후부터는 트랜스듀서를 이용해 복벽에서 울트라사운드 검사를 하는 것이 보통이다. 그러나 자궁경부에 어떤 이상이 있나 알아 보기위해 울트라사운드 검사를 할 때는 임신 제2 삼개월기 동안에도 울트라사운드 프로브를 질강에 넣고 울트라사운드 검사를 하기도 한다.
어떤 이유로 산전 초음파 검사를 할 때 소변을 보기 바로 직전의 태아의 자지가 꼿꼿이 서 있다가 소변을 다 본 후에는 자지가 더 이상 꼿꼿이 서 있지 않고 보통 크기로 줄어든 울트라사운드 영상을 볼 수 있다든지, 태아가 손가락을 입에 넣고 빠는 현상들을 초음파 검사 사진에 나타나기도 한다.
태반의 크기와 위치, 임신월수, 태아의 크기, 태아의 체위, 태아의 성별, 분만 예정일 추정, 선천성 기형의 유무, 태아의 병의 유무 등을 진단하기 위해 산전 울트라사운드(산전 초음파) 검사를 요즘 많이 하고 있다.
| 어떤 경우에 산전 울트라사운드(산전 초음파) 검사를 하나 |
산전 울트라사운드(산전 초음파) 검사는 검사의 비용이 비교적 적절하고, 초음파 그 자체로 인해 임산부에게, 또 태아에게 해가 되지 않기 때문에 임신 중 필요에 따라 많이 하는 검사이다. 그러나 여러가지 이유로 아무 때나 또 아무 경우나 이런 검사를 분별 없이 할 수는 없다.
위에서 이미 설명했지만, 산과에서는 기본적으로 하는 울트라사운드 검사, 특별한 이유가 있을 때 하는 선별적 울트라사운드 검사, 또는 태아에 관한 정보를 더 자세히 얻을 필요가 있을 때 하는 정밀 울트라사운드 검사 등으로 나누어 한다. 산전 울트라사운드 검사를 해야할 경우를 더 상세히 설명하면.
- 자궁내 임신이 됐는지, 자궁외 임신이 됐는지 확인할 때
- 분만 예정일이 언젠가 알아볼 때
- 임신 일수 또는 임신 주수에 따라 아기가 정상적으로 성장하는지 너무 큰지 너무 작은지 알아볼 때
- 아기에게 선천성 기형이 있는지 없는지 알아볼 때
- 단태, 쌍태, 또는 그 이상 다태인지 알아볼 때
- 임산부의 난소의 상태를 알아볼 때
- 임산부의 자궁의 상태를 알아볼 때
- 아기의 성장속도를 알아볼 때
- 아기의 심장 박동을 알아볼 때
- 양수의 양이 정상인지 너무 많은지, 또는 너무 적은지를 알아볼 때
- 태반이 붙어있는 자궁의 위치를 알아볼 때
- 태아의 뇌, 두골, 얼굴, 심장, 흉강, 복강, 복벽, 신장, 방광, 팔다리, 척주 등의 해부를 알아볼 때
- 아기의 성별을 알아볼 때
- 조기 분만이 될 위험성이 있을 때
- 임산부에게 당뇨병, 고혈압 등 어떤 병이 있을 때
- 질강을 통해서 양수가 나오거나 출혈이 생길 때
- 그 외
이상 열거한 여러 가지 경우에 관해 다음에 좀더 자세히 설명한다.울트라사운드 검사로 분만 예정일을 알아볼 수 있다. 이때 울트라사운드 검사를 임신 제 1 삼개월기에 해서 분만 예정일을 알아보는 것이 임신 제 2 삼개월기나 또는 임신 제 3 삼개월기에 해서 알아보는 것보다 더 정확성이 있다.
해부학적으로 어떤 이상이 태아의 요로, 복강, 팔다리, 척주, 뇌 등에 있나 알아보기 위해 임신 11-12주에도 산전 울트라사운드 검사를 할 수 있다.
단태 임신을 했는지 쌍태 임신을 했는지, 또는 그 이상 다태 임신을 했는지 울트라사운드 검사로 알아볼 수 있다. 또 쌍태 임신을 했을 때는 두 태아가 한 개의 태반을 가지고 있는지, 또는 각 태아가 태반을 따로 가지고 있는지 울트라사운드 검사로 알아볼 수 있다. 즉 융모막이 한개만 있는지 두개 있는지 알아볼 수 있다.
난소나 자궁의 해부학적 구조에 어떤 이상이 있나 알아볼 때도 임신중 울트라사운드 검사를 할 수 있다.
임신 15~16주에 울트라사운드 검사로 태아의 성별을 감별할 수 있다.
태아의 선천성 해부학적 기형을 울트라사운드 검사로 찾아낼 수 있다. 예를 들면 태아가 다운 증후군을 가지고 있는지 울트라사운드 검사로 확진할 수는 없다. 그러나 울트라사운드 검사로 태아가 다운 증후군에 걸려 있는지 알아보는데 많은 가치가 있다. 특히 요즘 산전 울트라사운드 “목덜미 반투명 스크린 검사( Nuchal translucency screen test)”를 해서 산전 다운 증후군을 진단하는 데 도움을 얻는다. 그러나 다운 증후군을 확실히 진단하기 위해서는 역시 양막천자로 얻은 양수로 염색체 검사 해야한다.
| 임신 중 언제 울트라사운드 검사를 해야 하나 |
울트라사운드 검사를 꼭 해야 하는지, 또는 언제 해야 하는지에 관한 의견은 산과, 주산기과, 방사선과의 전문의들간 의견 차이가 있다. 그러나 임신 20주 경에는 적어도 한 번 정도 산전 울트라사운드 검사를 해서 태아의 성장, 성별, 어떤 이상 등을 알아보는 것이 좋다고 한다.
울트라사운드검사로 목덜미 투명도 스크린을 해서 다운 증후군을 진단하기도 한다. 이 검사의 결과는 80%의 정확성이 있다고 한다.
태아의 간 등에서 알파-페토프로테인 (알파 태아단백, MSAFP)을 정상적으로 생성한다. 그 항원이 모체의 혈액 속으로 들어갈 수 있다. 임신 16~20주에 임신부의 피를 채취해서 임신부 혈청에서 알파-페토프로테인 농도를 측정할 수 있다.
임신부 혈청 알파-페토프로테인(임부 알파 태아 단백), 인간 코리오닉 고나도트로핀, 에스테리올 호르몬, 인히빈 A(Inhibin A) 등을 임신부의 혈청으로 검사해서 다운 증후군, 3 염색체성 13 증후군(Trisomy 13 Syndrome, 파타우 증후군), 3 염색체성 18(Trisomy 18 syndrome, 에드워드 증후군) 증후군을 진단하는 데 이용될 수 있다. 그러나 이 검사의 결과로만 확진하는 데는 이용할 수 없다.
Copyright ⓒ 2014 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
Routine or selective pregnancy tests and ultrasounds during pregnancy 임신 중 통상적으로 또는 선별적으로 받는 임상검사와 울트라사운드 검사
- During pregnancy, to find out whether the baby in the womb is growing well, what kind of genetic disease, and whether the baby has congenital malformations, and to check the health and well-being of the fetus and pregnant woman, clinical tests and Ultra Sound tests, etc.
- They are routinely or selectively performed, and sometimes special pregnancy tests are performed as needed.
- After pregnancy, when visiting a hospital for the first pregnancy check-up before delivery at the obstetrician, it is common to receive an initial checkup and receive necessary general clinical tests and general ultra-sound tests.
- These tests can be called basic pregnancy tests or routine pregnancy tests because they are routine pregnancy tests for almost all pregnant women.
- When a pregnant woman receives an initial examination, the weight and height of the pregnant woman are measured, vital signs such as pulse rate, respiration rate, body temperature, and blood pressure are checked, and appropriate physical examination is performed and a seismic examination is performed.
- The first pregnancy checkup before delivery, i.e. at the first pregnancy checkup, you will receive a blood test at the time of fertilization to check for anemia, and a urine chemistry test to see if there is sugar in the urine, proteinuria, hematuria or pyuria do.
- In addition, microscopic urine tests are performed, and urine bacterial culture tests are also performed if necessary.
- In addition, ABO blood type, Rh factor test, syphilis, AIDS test and rubella test, cervical cancer test (Hyundai test), etc. are performed.
- It is a general clinical test that performs these tests on a regular basis or as a basis. Thereafter, whenever a regular pregnancy check-up is performed before delivery, a clinical test can be performed normally or selectively according to the gestational week depending on the health status of the pregnant woman and the fetus.
The following blood tests are routinely done during pregnancy.
- A pregnant woman’s fertilization (CBC) test is done to see if she has anemia. Blood test for anemia in pregnant women A hemoglobin test, hematocrit, or fertilization test can be done to determine if the pregnant woman has anemia by collecting blood from the pregnant woman.
- ABO blood type and Rh factor in pregnant women. ABO blood type and Rh factor in pregnant women ABO blood type test is also performed, and the blood of pregnant women is routinely tested to test whether the RH factor is positive or negative.
- Rubella antibody test. Rubella antibody test A pregnant woman is tested for rubella antibodies to see if she has a history of rubella, and if so, to see if she has virus antibodies. Do a hepatitis B test.
- Hepatitis B test. A pregnant woman may be currently suffering from hepatitis B virus infection or may be carrying hepatitis B virus. During or after delivery, the baby can become infected with the hepatitis B virus. For that reason, hepatitis B antigen and antibody tests are routinely performed in the early stages of pregnancy to check whether a pregnant woman has hepatitis B, hepatitis B virus infection, and hepatitis B virus vaccination. . As soon as the baby is born from a mother who is pregnant with hepatitis B or carries the hepatitis B virus, the baby should be vaccinated against hepatitis B immediately and other appropriate treatment should be taken. Have a syphilis serum test.
- Syphilis Serum test.These days, it is rare for pregnant women to get syphilis. However, if a pregnant woman gets syphilis in the early stages of pregnancy, the pregnant woman’s fetus is infected with syphilis from the pregnant woman, and congenital anomalies can occur in the fetus. Or you can be born with a low impotence. All pregnant women should routinely undergo a syphilis serum blood test to determine if they have syphilis during early pregnancy.
- Have an AIDS blood test. Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection /AIDS test If you are infected with the human immunodeficiency virus while living a promiscuous sex life, you can get AIDS. You can also get infected with the virus through a dirty needle or medical device. And if you receive blood transfusions infected with the human immunodeficiency virus, you can get the disease. AIDS can develop in babies born to mothers infected with the human immunodeficiency virus.
- Blood glucose test and glucose tolerance test if necessary. Blood sugar in all pregnant women can be tested routinely or selectively. However, it is common to perform a blood glucose tolerance test selectively. Pregnant women can develop type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes, or pregnancy-induced diabetes. Pregnant women who did not have diabetes prior to pregnancy may develop diabetes due to pregnancy in pregnant women after pregnancy. This diabetic disease is called pregnancy-induced diabetes. Pregnancy-induced diabetes usually disappears spontaneously after childbirth. Gestation-induced diabetes is a type of pregnancy complication. To diagnose the disease, some doctors usually measure blood sugar every three months during pregnancy, by taking sugar and measuring blood sugar.
- Etc.
During pregnancy, if necessary, the following blood clinical tests and ultrasound tests are performed selectively.
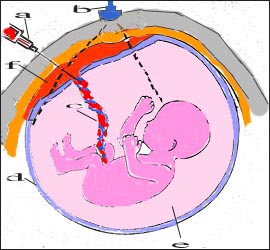
1. Amniocentesis

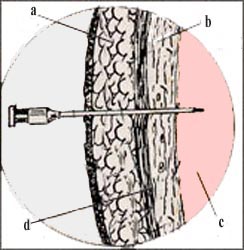
Abdominal wall anatomy a-skin, b-uterine wall, c-amniotic fluid, d-fascia
![]()

The cells of the fetus are contained in the amniotic fluid.
The fetal cells can be used to test the fetus’s chromosomes.
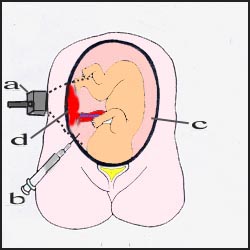
Part of amniotic fluid is drawn with a needle to test amniotic fluid a-UltraSound fixture, b-positive needle, c-positive, d-placenta ![]()
- The sac containing the fetus and amniotic fluid is called the amniotic sac, and the space is called the amniotic fluid.
- Until the baby is born, it is normal for the fetus to be immersed in the amniotic fluid contained in the amniotic sac. Sometimes, for some reason, the amniotic fluid is ruptured and there is no amniotic fluid. In this case, the fetus is not immersed in the amniotic fluid.
- The cells of the fetus that have fallen from the fetus are contained in the amniotic fluid.
- The amniotic fluid is punctured to collect a little bit of amniotic fluid, and the fetal cells in the amniotic fluid are cultured to test the fetal chromosome, and other clinical tests can be performed.
To perform such a test, a special needle is used to prick the abdominal wall, uterine wall, and amniotic sac membrane of a pregnant woman to extract the amniotic fluid contained in the amniotic sac.
- In what cases can amniocentesis be done?
- When the fetus has an abnormality that is dangerous to the life or health of the fetus When there is a possibility that the fetus may develop certain genetic diseases such as pancreatic cystic fibroma or Tay-Sachs disease, which are dangerous to the life or health of the baby in the future.
- When there is a possibility that the fetus has a disease caused by a chromosomal abnormality such as Down syndrome, trisomy 18 or trisomy 13 in the fetal ultra sound test
- When the maternal serum alpha fetoprotein test is performed selectively to determine if the fetus has Down syndrome, and the result is abnormally high.
- When fetal growth is delayed or abnormal Premature delivery due to amniotic fluid infection When a pregnant woman is infected with toxoplasmosis (toxoplasmosis) or is infected with cytomegalovirus or palbovirus, it can be said to be a high-risk pregnancy.
- At this time, the pathogen that caused the infectious disease in the mother can also infect the fetus. When the red blood cells of the fetus are destroyed due to Rh incompatibility To determine the degree of fetal lung development etc
- As described above, when diagnosing to find out what diseases the fetus has, when it is necessary to prevent such diseases from occurring, an amniotic fluid test can be performed for various reasons. The amniotic fluid test is of great importance and is often effective.
- An amniotic puncture can be harmful to the pregnant woman and the fetus, and it is a type of maternal invasion test, so it should be done only when absolutely necessary.
- Various health problems that can occur to a pregnant woman or fetus before, during, or after an amniotic puncture, why an amniotic puncture is essential,
and how the amniotic fluid test results obtained from an amniotic puncture are beneficial to the fetus, the baby to be born, or to the pregnant woman.
- After consulting with your doctor about what is harmful and harmful, you should carefully decide whether you should or should not perform an amniotic puncture. How to do an amniotic puncture Amniotic puncture is usually done at 15-20 weeks of pregnancy. However, you can do it after that as needed.
- Amniotic puncture can also be done in a private obstetrics and gynecology hospital. Occasionally, it can be done in hospitals where ultrasound tests and amniotic punctures are specially performed. After checking the amniotic sac with the uterine fetal ultrasound test, use a thin injection needle to extract about 15-20 cc of amniotic fluid in the amniotic sac.
- At this time, the tip of the needle passes through the skin layer, the subcutaneous layer, the muscle layer of the abdominal wall, the uterine wall, and the membrane of the amniotic sac in this order, and reaches into the amniotic sac.
- So it is common that the fetus in the amniotic sac is not damaged. When piercing the abdominal wall with an injection needle to perform an amniotic puncture, it can be a little uncomfortable and painful enough to occur when you get an injection.
- In general, you can complete the amniocentesis in 1 to 2 minutes without local anesthesia. The cells in the amniotic fluid obtained by amniocentesis are cultured in a cell incubator. A chromosome test is performed with the cells cultured in this way. It takes about 1 to 2 weeks to find out the results of the chromosome test. Sometimes a pregnancy test (FISH) is done to give the results within a day or two.
- Depending on the result, a diagnosis can be attached. However, the results are less accurate in diagnosing and usually require a more detailed examination again.
The dangers of amniotic puncture In very rare cases,
a miscarriage can occur, minor bleeding can occur, and amniotic fluid can leak into the vagina.
It can hurt a little when the needle is inserted.

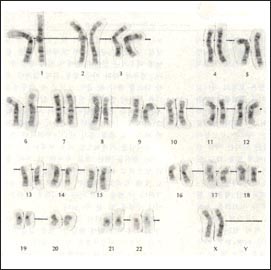
Photos of normal female autosomal and sex chromosomes
![]()
2. Ultrasound inspection

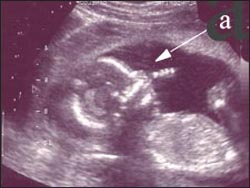
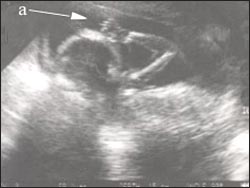
Prenatal ultrasound tests a-fetus is sucking a finger a-fetus is sucking a finger
![]()

Prenatal ultrasound tests a-fetus is sucking a finger a-fetus is sucking a finger
![]()
Types of UltraSound Test
The prenatal ultrasound test can be divided into a general prenatal ultrasound test, a selective ultrasound test for specific reasons, and a precise prenatal ultrasound test.
A general prenatal ultra-sound test checks the number of weeks of pregnancy, size and posture, heart rate, placenta location, and amount of amniotic fluid of the fetus.
When looking for abnormalities in certain organs, such as congenital heart anomalies in the fetus, it is common to do a precision prenatal ultra-sound test. In addition, various prenatal ultra sound tests can be performed as needed.
Principles of UltraSound Inspection
Ultrasound (ultrasound) of about 1 to 5 Megahertz can be produced from a probe attached to an ultrasound testing machine (ultrasound testing machine).
The vibrations of the ultrasound move into tissues such as fluids, soft tissues, and bones in the body. As the vibrations of the ultrasound move into each tissue in the body, it hits each tissue in the body. The hardness of the tissue is somewhat different for each type of tissue in the body. When the vibration of the ultrasonic wave hits a tissue with a very high hardness, the vibration no longer proceeds and the vibration is reflected.
When it hits a tissue with a very low hardness, the vibration continues to proceed and eventually it is also reflected. In other words, depending on the hardness of each tissue in the body, some of the ultrasound may be echoed earlier, some of the ultrasound may be vibrated more continuously, and eventually, depending on the hardness of the tissue hitting it, it may be echoed later.
In addition, some of the other ultrasonic waves can no longer vibrate and continue to vibrate until they have reverberated.
The distance from the probe attached to the ultrasound machine to the object to be inspected, the time at which the ultrasound is echoed, and the intensity of the echo are recorded on the recording paper of the inspection machine so that an ultrasound examination picture can be made to be seen with the naked eye. The ultrasound test was made using this principle.
Ultrasound tests are also done in the abdomen and in the vaginal cavity.
In medicine, the value that X-rays have given us humans is incalculable. In addition, the useful value that ultrasound tests give us humans is also incalculable in other fields as well as the whole medical field.
Especially in obstetrics and perinatal departments, the value of the ultrasound test is too great. When taking an ultrasound test, it does not cause pain to both fetuses and pregnant women, and this test is not an invasive test and is not harmful to the body of the test subject.
Depending on the number of weeks of pregnancy, an ultrasound probe is placed on the abdomen for examination, and during the first trimester during the first trimester of pregnancy, a special ultrasound probe is placed into the vaginal cavity for examination. After the first trimester of pregnancy, it is common to perform an ultrasound test on the abdominal wall using a transducer.
However, when performing an ultrasound test to find out what is wrong with the cervix, an ultrasound probe is placed in the vaginal cavity even during the second trimester of pregnancy and an ultrasound test is sometimes performed.
For some reason, when performing a prenatal ultrasound examination, the fetus’s cock right before urinating is standing upright.
- The phenomena of putting a finger in the mouth and sucking may appear on the ultrasound scan photos.
- Prenatal Ultrasound (Prenatal Ultrasound) is nowadays used
- to diagnose the size and location of the placenta,
- the number of months of pregnancy,
- the size of the fetus,
- the position of the fetus,
- the sex of the fetus,
- the estimated delivery date,
- the presence of congenital anomalies,
- and the presence of diseases in the fetus.
- In some cases, one prenatal ultrasound (prenatal ultrasound) test Prenatal Ultrasound (Prenatal Ultrasound) is a test that is often performed as needed during pregnancy because the cost of the test is relatively reasonable,
- and the ultrasound itself does not harm the pregnant woman or the fetus.
- However, for a number of reasons,
- it is not possible to perform these tests at any time and in any case without discernment. As explained above, in obstetrics,
- the basic ultrasound test, the selective ultrasound test when there is a specific reason, or the precise ultrasound test when you need to obtain more detailed information about the fetus, etc.
- Explaining in more detail the cases when prenatal ultrasound testing is required.
- When checking whether an intrauterine or ectopic pregnancy has occurred
- When we find out the expected delivery date sometime
- To find out whether your baby is growing normally, too large or too small, depending on the number of days or weeks of pregnancy
- When trying to find out if your baby has a birth defect When trying to find out if it is a single, twin, or more When to find out the condition of the ovaries in pregnant women
- When to check the condition of the uterus in pregnant women
- When looking at your baby’s growth rate When to check your baby’s heartbeat
- To find out if the amount of amniotic fluid is normal, too much, or too little When locating the uterus to which the placenta is attached
- When examining the anatomy of the fetus’s brain, skull, face, heart, chest cavity, abdominal cavity, abdominal wall, kidney, bladder, limbs, spinal column, etc.
- When to find out your baby’s gender When there is a risk of premature delivery When pregnant women have diabetes, high blood pressure, etc.
- When amniotic fluid or bleeding occurs through the vaginal cavity etc The various cases listed above will be described in more detail below:
- The expected delivery date can be determined by using an ultrasound test. At this time, it is more accurate to find out the expected delivery date by performing the ultrasound test in the first trimester of pregnancy than in the second trimester or in the third trimester of pregnancy.
- Prenatal Ultrasound tests can be done even at 11-12 weeks of pregnancy to find out what anatomical abnormalities are in the fetus’s urinary tract, abdominal cavity, limbs, spinal column, and brain. You can find out whether you have a single pregnancy, twin pregnancy, or more multiple pregnancies with an ultrasound test.
- Also, in twin pregnancy, you can check whether two fetuses have one placenta, or whether each fetus has a separate placenta with an ultrasound test. In other words, you can see if there are only one or two chorionic membranes.
- Ultrasound tests during pregnancy can also be done to check for any abnormalities in the anatomy of the ovaries or uterus. At the 15th to 16th week of pregnancy, an ultrasound test can be used to determine the sex of the fetus.
- Congenital anatomical malformations in the fetus can be detected by ultrasound testing. For example, an ultrasound test cannot confirm that a fetus has Down syndrome.
- However, it’s worth a lot to find out if your baby has Down syndrome with an ultrasound test. In particular, these days, prenatal ultra-sound “Nuchal translucency screen test” is used to diagnose Prenatal Down syndrome.
When should an Ultrasound test be done during pregnancy?
There are differences of opinion among obstetricians, perinatal and radiologists about whether or when an ultrasound test should be performed. However, it is said that it is good to do a prenatal ultra-sound test at least once in the 20th week of pregnancy to check the growth, sex, and any abnormalities of the fetus.
3. Nape of transparency screen Nuchal translucency screen
Down syndrome is also diagnosed by using a transparency screen at the nape of the neck with an ultrasound test. The results of this test are said to be 80% accurate. When performing a fetal ultra-sound test, it may appear on the test that there is an unusually higher amount of fluid accumulated in the back of the fetus’s neck. Lee Ryeon “It is more valuable in diagnosis if you use the nape transparency screen and other blood tests together. This test is one of the selective pregnancy tests.
4. Pregnant woman serum alpha-fetoprotein test
Pregnancy serum alfa fetoprotein test Alpha-fetoprotein (alpha fetoprotein, MSAFP) is normally produced in the fetal liver. The antigen can enter the mother’s blood. The blood of a pregnant woman can be collected at the 16th to 20th week of pregnancy and the level of alpha-fetoprotein in the pregnant woman’s serum can be measured. Maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein can also be found in the blood of normal pregnant pregnant women. However, the concentration may also increase when translocating a normal fetus, and may sometimes increase significantly when the fetus has dichotomous spine or spina bifida, or anencephalopathy, or when the fetus has other types of anatomical abnormalities. In addition, pregnant women’s serum alpha-fetoprotein levels may also increase when twins or more multiple pregnancy, early pregnancy bleeding, fetal abdominal wall malformation, Rh incompatibility, congenital nephrotic syndrome, and fetal death in the uterus. An audit of pregnant women’s serum alpha-fetoprotein levels is a type of screening test. So, if the result is quite high, it is usually confirmed by performing an ultra sound test or an amniotic fluid test.
5. In pregnant women, the following serological tests can be specifically and selectively performed.
Following tests can be done selectively during pregnancy Pregnancy’s serum alpha-fetoprotein (pregnancy alpha fetal protein), human corionic gonadotropin, esteriol hormone, and Inhibin A were tested with pregnant women’s serum. Trisomy 13 Syndrome (Patau syndrome) and Trisomy 18 syndrome (Edward syndrome) syndrome. However, it cannot be used to confirm only the results of this test. Inhibin A is produced by Sertoli cells in male testes and by granulosa cells in females. Down syndrome cannot be confirmed only by the Inhibin A concentration test, and when the result of such a screen test is abnormal, it is usually confirmed by performing a mineral water test or an ultra sound test. Serum blood tests are done to see if there are other genetic diseases. It is likely to be passed on to the fetus when there is a history of inherited diseases such as pancreatic cystic fibroma, Tay-Sachs disease, sickle cell disease, and hemophilia to a pregnant woman, her husband, or their family. In such a case, the blood of the pregnant woman or husband may be tested.
6. Examine the fetus’s blood by drawing it from the umbilical cord.

Umbilical cord blood test in fetus
Umbilical cord blood is collected from the umbilical cord in the uterus a-injection needle, b-ultra sound illuminator, c-umbilical cord, d-amniotic sac, e-amniotic fluid, f-placenta ![]()
When it is necessary to quickly diagnose infectious diseases caused by the fetus, fetal swelling due to blood type incompatibility, chromosomal abnormalities, fetal anemia, etc., blood is collected from the umbilical cord with an injection needle through the abdominal wall of the pregnant woman and tested for blood. In addition, when there is severe fetal anemia, blood transfusions are given to the fetus through the umbilical cord blood vessels. You can do these tests after 18 weeks of pregnancy. When collecting blood from the umbilical cord, do it while performing an ultra sound test. Complications such as abortions and fetal infections can rarely occur with this test.
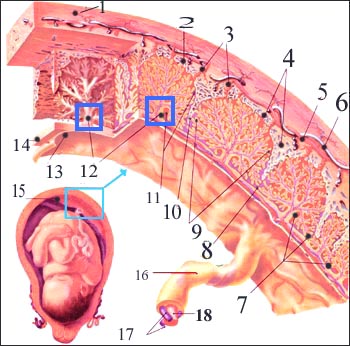
7. Examine the villi (Chorionic villi).

Chorionic villi test Placenta blood circulation and villi 1-uterine muscle layer, 2-superior deciduous membrane, 3-linear artery, 4-venous sinus, 5-uterine artery, 6-uterine vein, 7-nutritional germ layer, 8-주연호, 9-capillaries of the fetus, 10-superior deciduous septum, 11-chorionic liver, 12-progenitor chorion, 13-amniotic membrane, 14-chorionic valve, 15-주연호, 16-umbilical cord, 17-umbilical artery, 18-umbilical vein Source-Ross Laboratories, Columbus. Ohio. USA
Inner and outer cell groups are formed in fertilized eggs. Embryos are formed from the inner cell group and placenta from the outer cell group. The placenta contains the chorionic villi (Chorionic villi) tissue. Hereditary diseases can be diagnosed by examining the chromosomes of cells in the chorionic villi. The chromosomes of cells in the chorionic tissue are identical to those in the cells of the fetus. Part of the chorionic villi can be acquired to find out what is wrong with the fetus’s chromosomes or to diagnose what kind of hereditary disease. This method is called chorionic villi sampling. A biopsy can be performed with chorionic villi at around 10-20 weeks of gestation. This test can be performed by collecting a part of the chorionic villi with a small needle through the abdominal wall of the pregnant woman, or by collecting the chorionic villi with an injection needle through the vaginal cavity. When taking a sample of chorionic villi required for this test, a part of the chorionic villi is collected while checking the location of the placenta attached to the uterus with an ultrasound test. The chromosomes can be tested with live villi collected by this test. This test can be done to see if the baby has a genetic disease in the baby’s mother and father. It takes 1 to 3 weeks for the results of the test to come out. When testing for genetic diseases, it is common to also test the DNA of cells obtained from the villi. This test is one of the invasive pregnancy tests, and side effects such as infection, uterine bleeding, and abortion can occur infrequently.
8. Triple marker test
The triple marker test is called a triple marker test, a triple test, or a triple marker test. This test is done with the pregnant woman’s blood at around 16-18 weeks of pregnancy. This test can be performed selectively when a fetal neural tube defect or Down syndrome is suspected. There is a diagnostic value of 60%, but it is not effective in diagnosing fetal malformations.
9. Fetal congenital heart disease
Nowadays, the fetus is diagnosed for congenital malformations and, if necessary, intrauterine fetal surgery is performed. It is possible to diagnose the presence or absence of cardiac abnormalities in the fetus using the ultrasound cardiac dynamics method.
The type of heart malformation found in the diagnosis and Depending on the degree, the treatment method for heart malformation was also selected. To successfully achieve your goals here, pregnancy-fetal medicine, pediatric cardiologists, perinatology Inquiries, neonatal surgeons, etc.
A fetal cardiac diagnosis treatment team is absolutely necessary.
When you have congenital heart malformations in your family When pregnant women have diabetes When you have systemic lupus erythematosus (loops)
When the amniotic fluid test is abnormal During pregnancy when exposed to certain drugs It is recommended to check for any abnormalities in the fetus’s heart pregnancy. (Reference; New York-Presbyterian Children’s Health. Spring 2008). Copyright ⓒ 2014 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-본 사이트의 내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
“Parental education is the best medicine.“