여성의 골반 구조와 임신 Anatomy of female pelvis and pregnancy
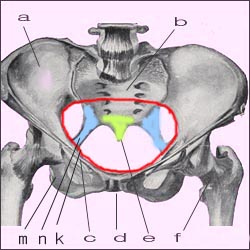
여성의 골반강
a-장골, b-천추, c-쿠퍼인대, d-치골결합, e-미추, f-대퇴골. k-골반강의 입구(적색 원), m-치골, n-천극인대
참고문헌-Principles and Practice of Obstetrics, De Lee-Greenhill, 9th Edition, Saunders
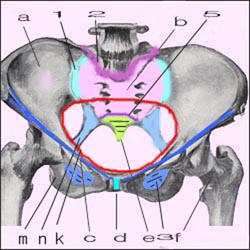
여성의 골반강과 골반에 있는 각종 인대와 결합
a-장골, b-천골, e-미골, f-대퇴골, m-치골 n-천극인대, c-쿠퍼인대, 3-폐쇠막 1-천골 장골관절, 2-요척추 천골관절, 5-천골 미골관절, d-치골결합 k-골반강 입구
참고문헌-Principles and Practice of Obstetrics, De Lee-Greenhill, 9th Edition, Saunders
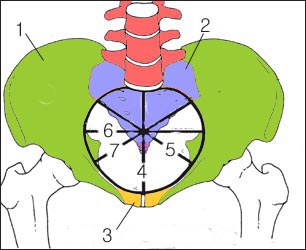
골반강의 내구
1-장골, 2-천추, 3-치골, 4-전후직경, 5-좌우직경, 6과 7-사경직경
1-장골, 2-천추, 3-치골, 4-전후직경, 5-좌우직경, 6과 7-사경직경
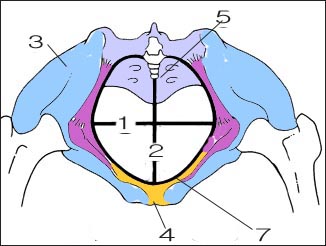
골반강의 외구(7)
1-좌우직경, 2-전후직경, 3-장골, 4-치골, 5-미골
![]()
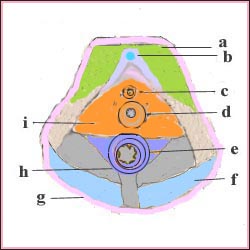
여성 골반저의 해부도와 근육
a-치골 결절, b-음핵, c-요도, d-질문, e-항문 근육 f-외항문 괄약근, g-주피, i-질부 근육
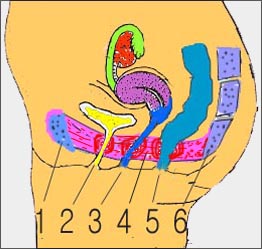
여성 골반저 근육와 골반강내 장기
1-치골, 2-요됴, 3-질, 4-골반저 근육, 5-직장, 6-미골과 천추 근육
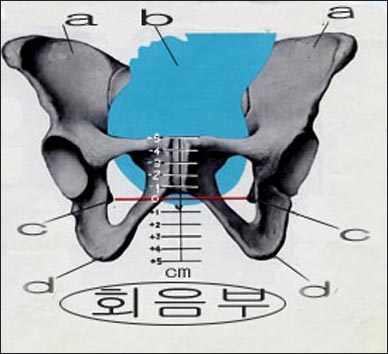
분만 중 태아 선진부 하강도
a-장골 능, b-태아 선진부, 여기서는 머리, c-좌우 골극, d-좌골 조면
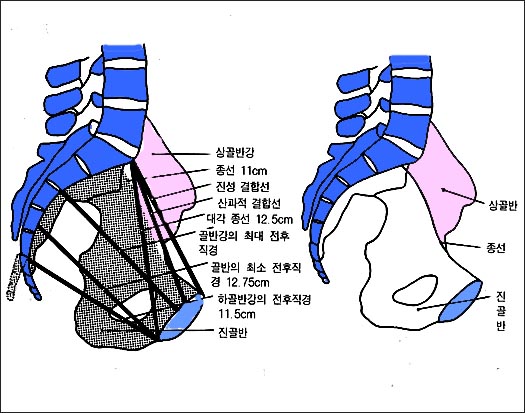
여성 골반강 평면에 있는 여러가지의 직경
아기를 자연으로 분만할 수 있나 알아보기 위해 임산부의 골반강의 평면 직경을 알아 볼 수 있다.
Anatomy of the female pelvis and pregnancy 여성의 골반 구조와 임신

A pelvic cavity in women
a-iliac spine, b-sacral spine, c-cooper ligament, d-pubic linkage, e-coccyx, f-femur. k-entrance to the pelvic cavity (red circle), m-pubis, n-celestial ligament References-Principles and Practice of Obstetrics, De Lee-Greenhill, 9th Edition, Saunders

Combined with various ligaments in the pelvic cavity and pelvis of women
a-iliac bone, b-sacrum, e-coccyx, f-femur, m-pubic n-sacral ligament, c-cooper ligament, 3-closing membrane 1-sacral iliac joint, 2-lumbar sacral joint, 5-sacral coccyx Joint, d-public joint, k-pelvic cavity entrance References-Principles and Practice of Obstetrics, De Lee-Greenhill, 9th Edition, Saunders

The inner pelvic cavity 1-Ilium, 2-Sacrum, 3-Pibular, 4-Anterior and posterior diameter, 5-Left and right diameter, 6th and 7-사경

Outer opening of the pelvic cavity (7) 1-left and right diameters, 2-anterior and posterior diameters, 3-iliac bones, 4- pubis, 5-coccyx

Anatomy and muscles of the female pelvic floor
a-pubic bone, b-clitoris, c-urethra, d-vaginal orifice, e-anal muscle f-external anal sphincter, g-주피, i-vaginal muscle

Female pelvic floor muscles and organs in the pelvic cavity
1-pubis, 2-urethra, 3-vagina, 4-pelvic floor muscles, 5-rectum, 6-coccyx and sacral muscles

Descent of the advanced fetus during delivery
a-iliac crest, b-fetal advanced part, here head, left and right osteophytes, d-sciatic rough surface

Different diameters in the plane of the female pelvic cavity
To see if the baby can be delivered naturally, the planar diameter of a pregnant woman’s pelvic cavity can be determined.
Copyright ⓒ 2014 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
“Parental education is the best medicine.“